Spring 2007
week 6: 2/23
Hello my friends,
I'm happy with the way class went last night. I know that 3 hours to spend on JavaScript is a long time to spend anytime, particularly on Friday night, but you all did well with the material we covered last night. However, we won't always have enough in class to do the homework that should've been done the week before as we did last night in the beginning of class. For those of you who haven't been checking the blog or doing your homework (and there are quite a few of you), your grades are already suffering. So, please try not to forget to do your homework. It is a big part of the grade for this class, and it will help you to understand what we do the next week in class.
That being said, let's get down to business: creating a bar graph on-the-fly. In this posting, I will continue from the previous posting. Although it was a rather difficult script we wrote last week compared to others we have done so far in class, it was actually the first real and useful application of JavaScript we have seen. We didn't simply learn about a particular statement type or term, such as conditional statements or variables and use them in a couple examples. NO, we actually put to use much of what we have learned so far into an actual script that has real benefit. We didn't just figure out if a number was odd or even, we magically created and modified web-content in the form of an instant and colorful bar graph with little more than a JavaScript script.
Although I cannot say that things will get any easier from here, I can certainly say that they will not get any more difficult. Because it had so many parts, and because it involved a form, that was one of the more difficult scripts we will contend with during this entire term. Moreover, it has a great many similarities to the form validation that we will start to cover in a couple weeks, and which you will use on your final project. As a result, some of what we did last week, you will see again (and again) in class, and hopefully then it won't be quite as hard as it was the first time.
And finally, I want to inform everyone not to miss class next week (Friday, March 2) as I will be explaining the first part of the mid-term project on which we will spend time in class working. In this week's posting, you will see below I have a link for the take-home mid-term exam. Carter-
I'm happy with the way class went last night. I know that 3 hours to spend on JavaScript is a long time to spend anytime, particularly on Friday night, but you all did well with the material we covered last night. However, we won't always have enough in class to do the homework that should've been done the week before as we did last night in the beginning of class. For those of you who haven't been checking the blog or doing your homework (and there are quite a few of you), your grades are already suffering. So, please try not to forget to do your homework. It is a big part of the grade for this class, and it will help you to understand what we do the next week in class.
That being said, let's get down to business: creating a bar graph on-the-fly. In this posting, I will continue from the previous posting. Although it was a rather difficult script we wrote last week compared to others we have done so far in class, it was actually the first real and useful application of JavaScript we have seen. We didn't simply learn about a particular statement type or term, such as conditional statements or variables and use them in a couple examples. NO, we actually put to use much of what we have learned so far into an actual script that has real benefit. We didn't just figure out if a number was odd or even, we magically created and modified web-content in the form of an instant and colorful bar graph with little more than a JavaScript script.
Although I cannot say that things will get any easier from here, I can certainly say that they will not get any more difficult. Because it had so many parts, and because it involved a form, that was one of the more difficult scripts we will contend with during this entire term. Moreover, it has a great many similarities to the form validation that we will start to cover in a couple weeks, and which you will use on your final project. As a result, some of what we did last week, you will see again (and again) in class, and hopefully then it won't be quite as hard as it was the first time.
And finally, I want to inform everyone not to miss class next week (Friday, March 2) as I will be explaining the first part of the mid-term project on which we will spend time in class working. In this week's posting, you will see below I have a link for the take-home mid-term exam. Carter-
- TOPICS:
- HOMEWORK
- LINK Mid-Term Exam—due in three weeks.
For extra credit in the exam, please see directions for a script below:
- Create a script that requests a number from the user in a prompt() function or in a form element (as in Friday's class;
- It should utilize a for() loop that loops the same number of times as the user's number—see the book for instructions on how to create a for() loop;
- The for() loop should repeat an alert() function for each loop with a message inside such as this:
Click Here to see example:
- Create a script that requests a number from the user in a prompt() function or in a form element (as in Friday's class;
- LINK Mid-Term Exam—due in three weeks.
- LINK Mid-Term Project—also due in three weeks, check blog during week for additional reading material to download for this project. I have yet to cover most of requirements for this project; however, I will address each issue in the next two classes.
- LINK Reading—Download this reading by clicking on the LINK and. It will assist you in creating the Multiplication Table.
- Review:
- document.getElementById()—This is a JavaScript built-in function that selects the specified ID from the HTML code in the body of the document and that enables the script to manipulate it in some way. For example, if there is an ID by the name of "homework", the document.getElementById function may select it in this way:
document.getElementById("homework").
As a result, the script will activate the "homework" ID and then have the ability to do things with it or extract data from it. If it is an H1 tag or a H2 tag or a P tag, it may change the color of the text, or the size or various other properties. If it is a form element, it may be able to extract the data from it. It does so in this way: document.getElementById("homework").value, where value is whatever is typed in the blank of the form element with that ID.
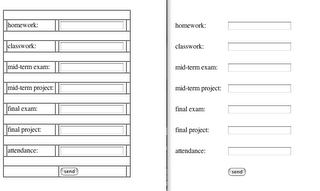
In the form we typed last week, there were seven (7) form elements. We were able to extract whatever data the user types in those seven blanks with this new function. Below I create seven new variables, and then use the document.getElementById() function to move the data from the form elements into the variables. Finally, all is revealed with a series of alert() functions.
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript">
<!--
function writeText()
{
var homework = document.getElementById("hw").value;
var classwork = document.getElementById("cw").value;
var mtExam = document.getElementById("mtE").value;
var mtProject = document.getElementById("mtP").value;
var fExam = document.getElementById("fE").value;
var fProject = document.getElementById("fP").value;
var quiz = document.getElementById("q").value;
alert(homework);
alert(classwork);
alert(mtExam);
alert(mtProject);
alert(fExam);
alert(fProject);
alert(quiz);
}
//-->
</script>
- Event Handlers—In JavaScript there are a series of terms that cause things to happen, much like built-in functions; however, unlike them, event handlers make things occur as a result of certain 'computer events'. These events are peculiar to computers, events such as loading a browser window or web-page, or closing a web-page or browser window, such as clicking with the mouse or moving the cursor with the mouse. These are all events which occur in a computer environment. Event handlers use these events to cause other things to occur, such as making something appear or disappear when you click on a button with a mouse. The click of the mouse is the event that the event handlers handle. The appearance of a pop-down menu when you click on the mouse is the action that the event handlers cause to occur. Some common event handers are: onLoad, onUnload, onmouseOver, onmouseOut, onClick, etc.
Like the <a> anchor tag, event handlers can be used to call or activate user-defined functions. We can use an event handler to activate our function above with the submit button in our form. We do this in the <input/> tag itself:
<tr>
<td colspan="3"> </td>
<td>
<input type="button" id="myButton" value="send" onclick="writeText()"/>
</td>
<td> </td>
</tr>
- document.getElementById()—This is a JavaScript built-in function that selects the specified ID from the HTML code in the body of the document and that enables the script to manipulate it in some way. For example, if there is an ID by the name of "homework", the document.getElementById function may select it in this way:
- INTRODUCE: Images—As you already know, the document.write() function allows us to write data such as strings and numbers directly into a web-page, and that HTML tags can be included to format a page as any ordinary web-page. Up to now, we have only used text and numbers and formatted them with HTML; however, the <img/> tag is also HTML, so it may also be written into a page. Here is an example:
document.write("img src = ‘images/ myPicture.jpg’ alt = ‘my picture’/>")
Whatever the image is, it will now appear in the page if this statement is run in a script. But more can be done: in addition to the src and alt attributes for the <img/> tag are the width and height attributes. Knowing this gives us the opportunity to make the image size customizable depending on numbers input into the script. If we use the form from last week's class which request numbers, grades for each of the input blanks, we can adjust the size of the images with them. If each of the images is set to have the same height, say 10 pixels, but adjustable widths, then depending on the numbers input into the blanks we can change the widths of images.
Type some numbers in the blanks below, then click submit to see how this operates.How this works is not some magical mystery when you understand that everything written into a page such as this is a combination of plain text and HTML. You already know HTML, now all you need to do is find out how JavaScript put it there.
- The first step is to use ideas from the bit of script we already have, but instead of using the alert() function, we will use document.write() Further, instead of using seven variables and seven form fields, I will stick to just the two that I have above. Here is a comparison of how we left off in the last posting here, and how we're beginning in this one:
OLD:
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript">
<!--
function writeText()
{
var grade1 = document.getElementById("g1").value;
var grade2 = document.getElementById("g2").value;
alert(grade1);
alert(grade2);
}
//-->
</script>
NEW:
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript">
<!--
function writeText()
{
var grade1 = document.getElementById("g1").value;
var grade2 = document.getElementById("g2").value;
document.write(grade1);
document.write(grade2);
}
//-->
</script>
As you can see, all that has been alterred is that the alert() function has been changed to the document.write() function.
- Now that we have done this, we can add the HTML, meaning the images. See the revised document.write() functions below:
document.write("<img src=‘images/sky.gif’ alt=‘grade one’ height=‘10px’ width=‘10px’/>" + grade1);
document.write("<img src=‘images/purple.gif’ alt=‘grade one’ height=‘10px’ width=‘10px’/>" + grade1);
In addition to adding the image, I've used the alt, the src, the width, and the height attributes.
- Currently, the width and the height are set values of 10 for each image. They can, nonetheless, be made to vary depending on the values input at the form elements. Remember, the values typed into the form elements are stored in variables of the same names: grade1 and grade2. Those variables can be used as the value of the width attributes.
Look closely at the example below, especially at the use of double-quotes (" ") and single-quotes (‘ ’).
document.write("<img src = ‘images/sky.gif’ alt = ‘grade one’ height = ‘10px’ width = ‘" + grade1 + "px’/>" + grade1);
document.write("<img src = ‘images/purple.gif’ alt = ‘grade two’ height = ‘10px’ width = ‘" + grade2 + "px’/>" + grade2);
As a result of this revision, the height attribute for both images is set at 10 pixels but the width is set to some value grade1 or grade2. If the user types in 88 or 23, then that will be the new width of the image. Since my images are tiny .gif images created in Photoshop with only 1px in width and only 1px in height, when the width and height attributes of the <img/> tag are adjusted, they can become any size. The advantage is that the file size remains unchanged no matter what size the image become in the HTML document as a result of the script.
- If you revisit the function above, you will see that there is one bar for each input box, but that there is also third bar labelled average. Obviously, then, this is the average of the two grades entered into the blanks in the form above.
To recall elementary school mathematics, to take an average of several numbers is to add up all the numbers and then dvide by how many numbers there are, such as: (A + B + C)/3 or (A + B + C + D)/4. In the example for the script in this page, there are only two numbers, grade 1 and grade 2. To average them out, we simply add them together and then divide by two: (grade1 + grade2)/2. Therefore, we will revise the script again by adding a third variable with the average of the first two variables as its value:
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript">
<!--
function writeText()
{
var grade1 = document.getElementById("g1").value;
var grade2 = document.getElementById("g2").value;
var average = (grade1 + grade2)/2;
document.write("<img src = ‘images/sky.gif’ alt = ‘grade one’ height = ‘10px’ width = ‘" + grade1 + "px’/>" + grade1);
document.write("<img src = ‘images/sky.gif’ alt = ‘grade two’ height = ‘10px’ width = ‘" + grade2 + "px’/>" + grade2);
document.write("<img src = ‘images/purple.gif’ alt = ‘average’ height = ‘10px’ width = ‘" + average + "px’/>" + average + " average");
}
//-->
</script>
In the above script, we've added a third variable and a third document.write(). However, you'll soon see, that if you run the script, the third document.write() will give you a very large number. This is because when the first two numbers are added together, concatenation is used instead of addition. Therefore, the numbers are put one right after the other instead of creating a sum, and 36 + 78 = 3678 instead of 114. This means that when the user types into the form fields, the data entered is string data even if numbers are used.
- To solve this problem, the data entered into the form fields must immediately converted from strings into numerical values. This is done, if you recall, by using the parseInt() function. To use this function, data or a data container is put between the parentheses of the function. One possible solution is as follows:
var grade1 = document.getElementById("g1").value;
var temp1 = parseInt(grade1);
var grade2 = document.getElementById("g2").value;
var temp2 = parseInt(grade2);
This would solve the problem; however, it would also require the creation of 2 more variables-- temp1, temp2--and this is a bit repetitive and redundant.
There is a way, however, to make a more efficient solution: convert the value with parseInt() before it gets put into the first variables, (grade1, grade2). This would eliminate the need for the temp1, temp2 variables. As it is now,
first, the value is put in the variable grade1 or grade2; and
second, the value in the variable is converted by parseInt().
But it would be much easier if we could parseInt() the value before it is put into the variable grade1 or grade2 instead of after.
- This is resolved by examining how we initialize our variables:
variable value
var
grade2 = document.getElementById("g2").value;
We see that the value comes from the ID of the form element, and then it is put into the variable with the assignment operator (=). The easiest thing to do to convert the string value to a numerical value, would be simply to put it into the parseInt function like so:
var grade2 = parseInt(document.getElementById("g2").value );
Notice that the whole statment -- document.getElementById("g2").value -- is placed between the parentheses of the parseInt() function. That is because that whole thing is what represents the value in the form field.
- The next thing we must do is make certain that we prevent anyone from typing anything in the form fields other than numerical values, as non-numbers will get NaN as a return value, Not a Number. To do this we use a conditional (if...else) statment, but we must make sure of two things, that grade1 is a number AND that grade2 is also a number; however, we actually have to ask the question backwards, if it is NOT a number instead of if it IS a number. The distinction is important because we use a special built-in function for it, isNaN(), which asks whether a given value is NOT a number. If the value IS NOT a number, then the function returns true, and so, predictably, if the value IS a number, then the function returns false. This will work well with a conditional statement, which, if you remember, has the following form:
if(condition)
{ // runs if condition is true
statement;
statement; etc.
}
else
{ // runs if condition is false
statement;
statement; etc.
}
Since the condition runs on boolean data, must be either true or false, and since the isNaN() results in boolean data, then we can put the isNaN() function inside the condition, as follows:
if(isNaN(data value))
Therefore, if the data value above is not a number then isNaN() will return true. If isNaN() returns true, then the condition will be true and the first part of the if...else statement will be run. If, on the other hand, the data value is a number, then isNaN() will return false, and the condition will be false. This means that the else part of the if..else statement will be run.
In order for this to work for us properly, we should stop the script from running, or, more specifically, we should stop the document.write() part of the script from running unless the user types in ONLY numbers in the form fields. Since the isNaN() function returns true only if the data is NOT numerical, then the true part of our conditional (if...else) statement should be an alert() telling the user to type in only numbers:
if(isNaN(document.getElementById("g1").value))
{
alert("You must type NUMBERS only")
}
and the false part of our conditional statement will contain the document.write()
else
{
document.write("<img src = ‘images/sky.gif’ alt = ‘grade two’ height = ‘10px’ width = ‘" + grade2 + "px’/>" + grade2)
}
- But we must remember that we have TWO conditions: 1) grade1 must be a number; 2) grade 2 must also be a number. Therefore we will have to use the OR operator within the condition as follows:
if(isNaN(document.getElementById("g1").value) ||isNaN(document.getElementById("g1").value))
The addition of this operator makes certain that if either one condition or the other is false, then the WHOLE condition of the if() statement is false, and the else statements get run instead. Nearing completion, then, the whole script looks like this:
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript">
<!--
function writeText()
{
var grade1 = parseInt(document.getElementById("g1").value);
var grade2 = parseInt(document.getElementById("g2").value);
var average = (grade1 + grade2)/2;
if(isNaN(document.getElementById("g1").value) || isNaN(document.getElementById("g2").value))
{
alert("Please type only NUMBERS!");
}
else
{
document.write("<img src = ‘images/sky.gif’ alt = ‘grade one’ height = ‘10px’ width = ‘" + grade1 + "px’/>" + grade1);
document.write("<img src = ‘images/sky.gif’ alt = ‘grade two’ height = ‘10px’ width = ‘" + grade2 + "px’/>" + grade2);
document.write("<img src = ‘images/purple.gif’ alt = ‘average’ height = ‘10px’ width = ‘" + average + "px’/>" + average + " average");
}
//-->
</script>
- Finally, we can concern ourselves with where the script writes the code containing the images. Up until now, we have used the document.writefunction, but there is another way: if you wish to write code and text into the current document instead of a new document, then you have to place it in between a pair of pre-existing HTML tags with its own ID.
The best candidate for this is a pair of<div> </div> tags. These tags are ideal for a few reasons: 1) because they are block-level tags; 2) because they can be used to create layers; 3) because they do little to affect the page by themselves without anything (text or otherwise) between them, which means you can place a pair of <div> </div> tags in a page of HTML code without affecting it much. They can sit there invisibly within the code with their ID waiting to receive directions from a JavaScript to write text or code between them, like so: <div id="graphLayer"> </div>. As you already know, this ID can be called upon using the built-in function, getElementById(). Unlike our previous uses of this function with form elements, we are not asking for its value. Instead, we want to place some code between the tags. Therefore, instead of .value, we place .innerHTML afterwards like so: document.getElementById("graphLayer").innerHTML. Knowing this, all we have to do next is define what it is we want to go between those tags, and as mentioned before, we want to put the code from the three document.write() functions there:
document.getElementById("graphLayer").innerHTML
= "<img src = ‘images/sky.gif’ alt = ‘grade one’ height = ‘10px’ width = ‘" + grade1 + "px’/>" + grade1 +
"<br/><img src = ‘images/sky.gif’ alt = ‘grade two’ height = ‘10px’ width = ‘" + grade2 + "px’/>" + grade2 +
"<br/><img src = ‘images/purple.gif’ alt = ‘average’ height = ‘10px’ width = ‘" + average + "px’/>" + average + " average";
- Currently, the width and the height are set values of 10 for each image. They can, nonetheless, be made to vary depending on the values input at the form elements. Remember, the values typed into the form elements are stored in variables of the same names: grade1 and grade2. Those variables can be used as the value of the width attributes.
- The first step is to use ideas from the bit of script we already have, but instead of using the alert() function, we will use document.write() Further, instead of using seven variables and seven form fields, I will stick to just the two that I have above. Here is a comparison of how we left off in the last posting here, and how we're beginning in this one: